One small step for man, one giant leap for the Pittsburgh startup community comes as Astrobotic completes yet another successful test of its lunar lander.
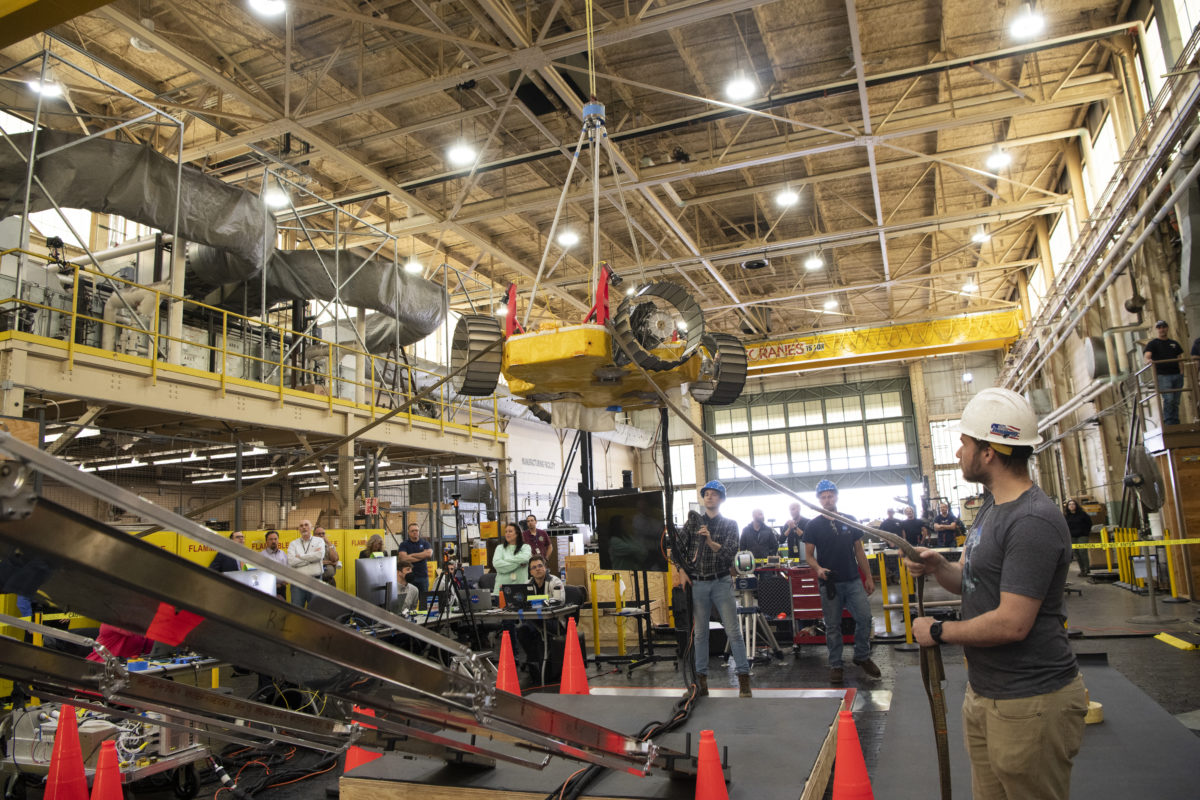
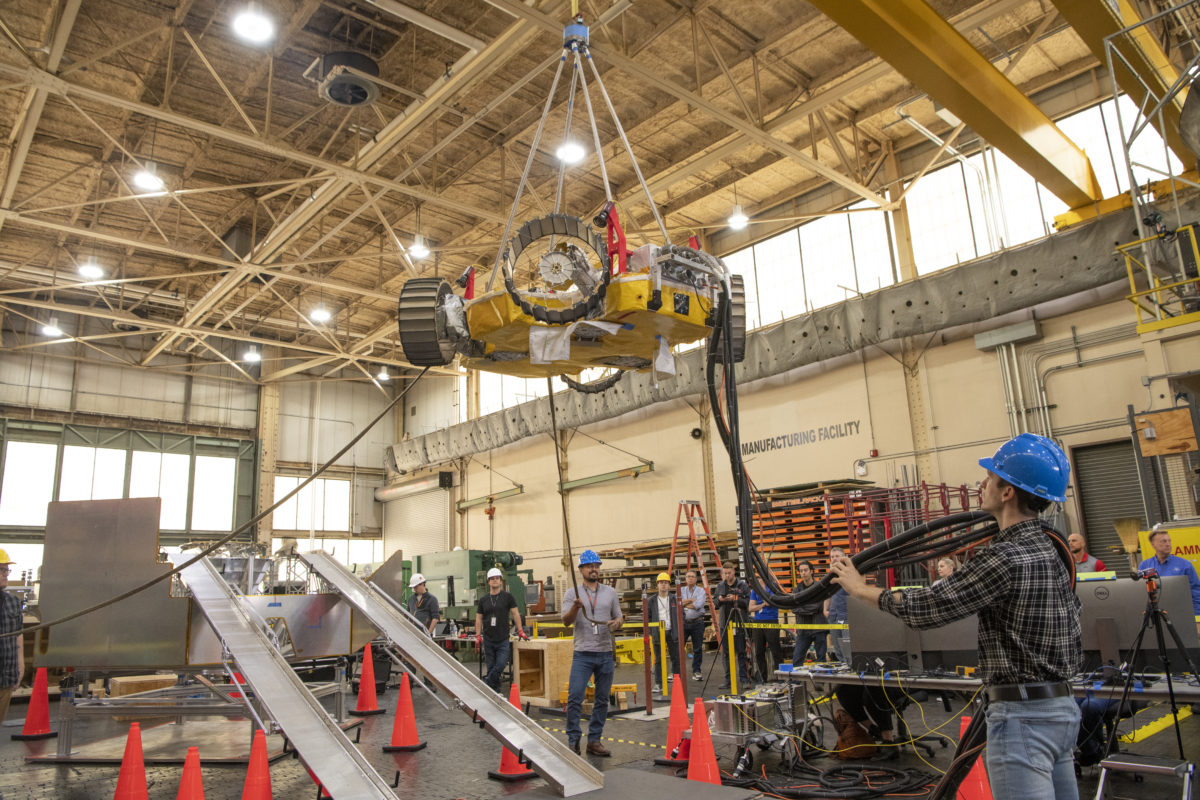
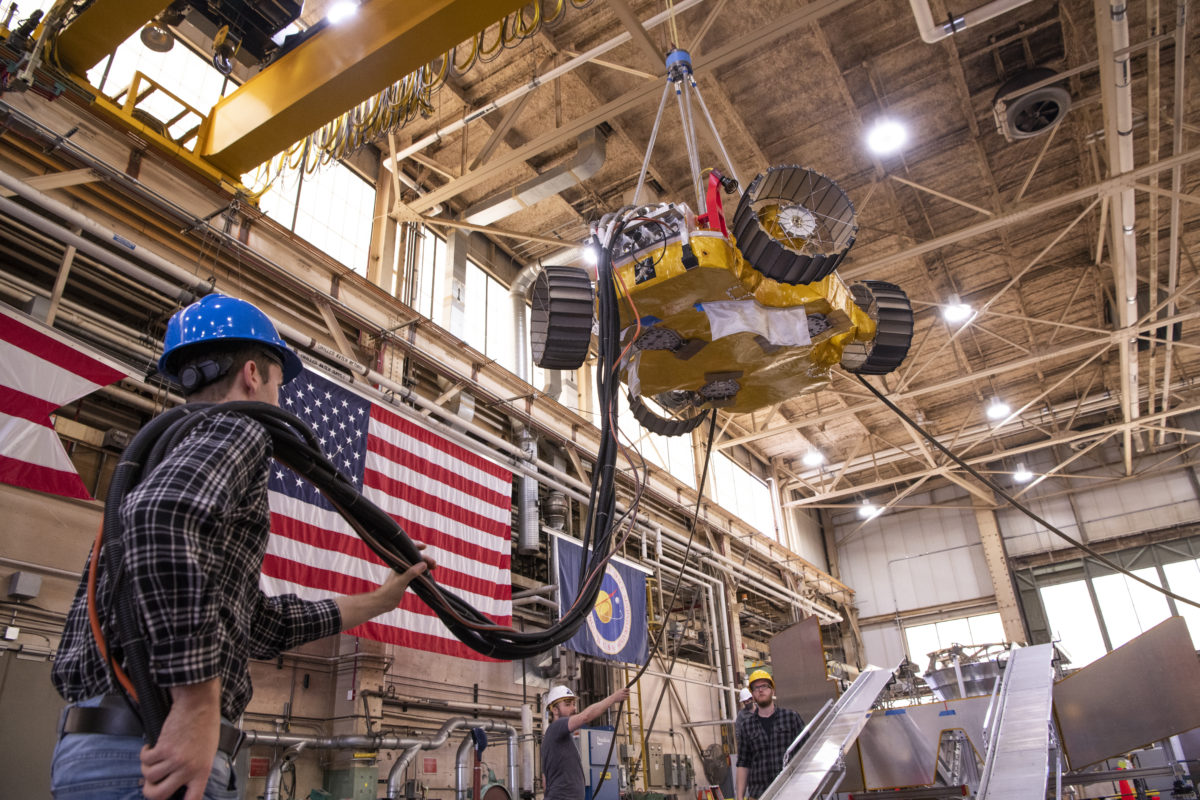
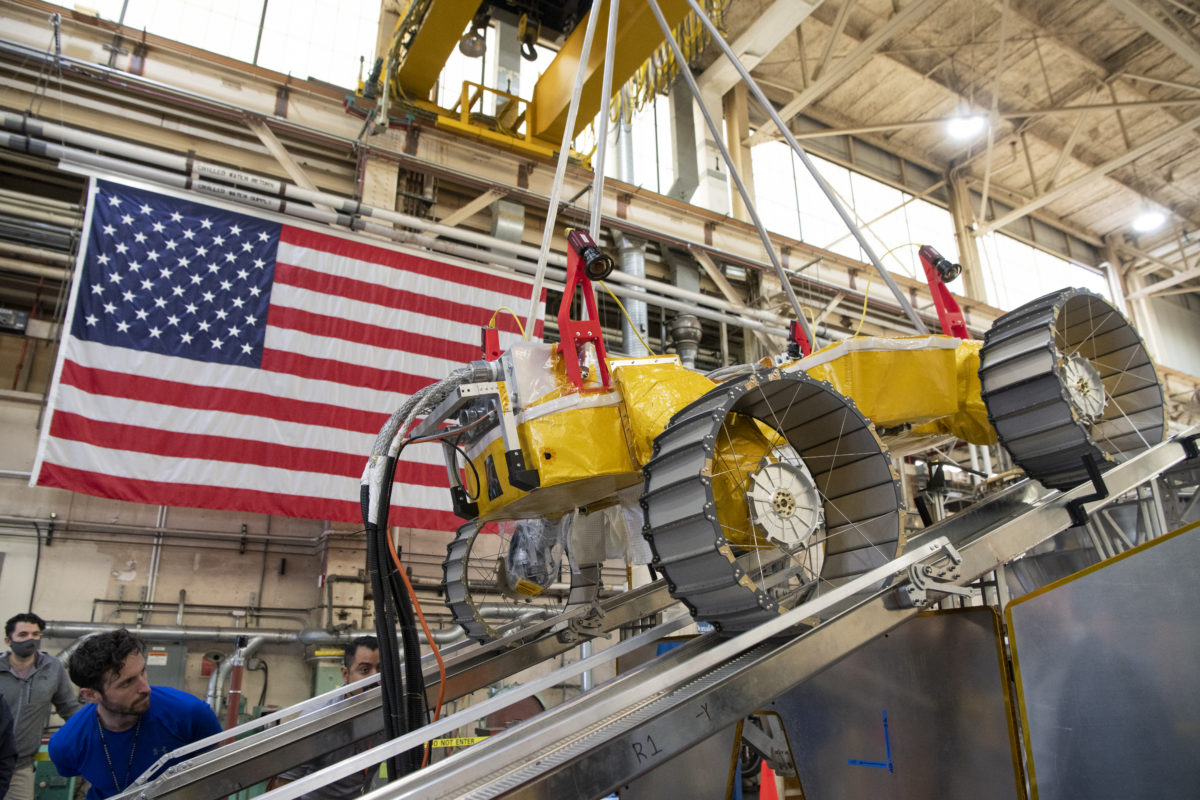
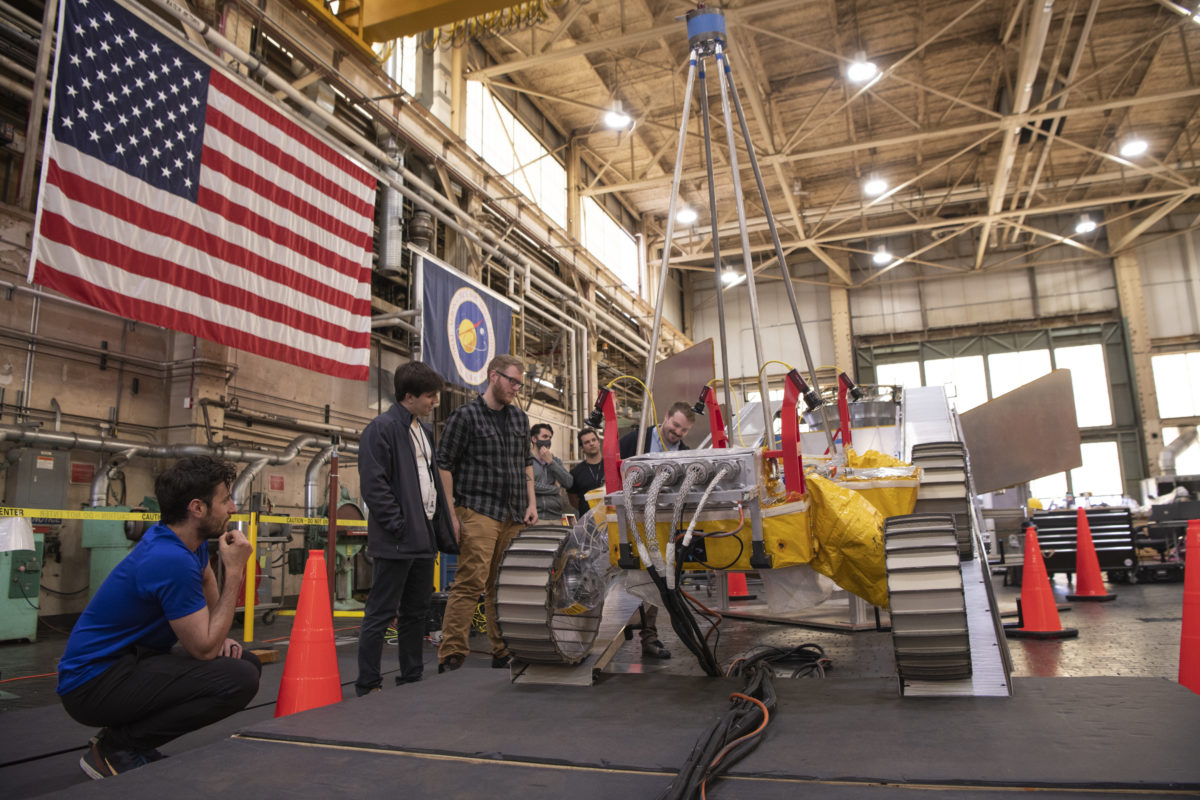
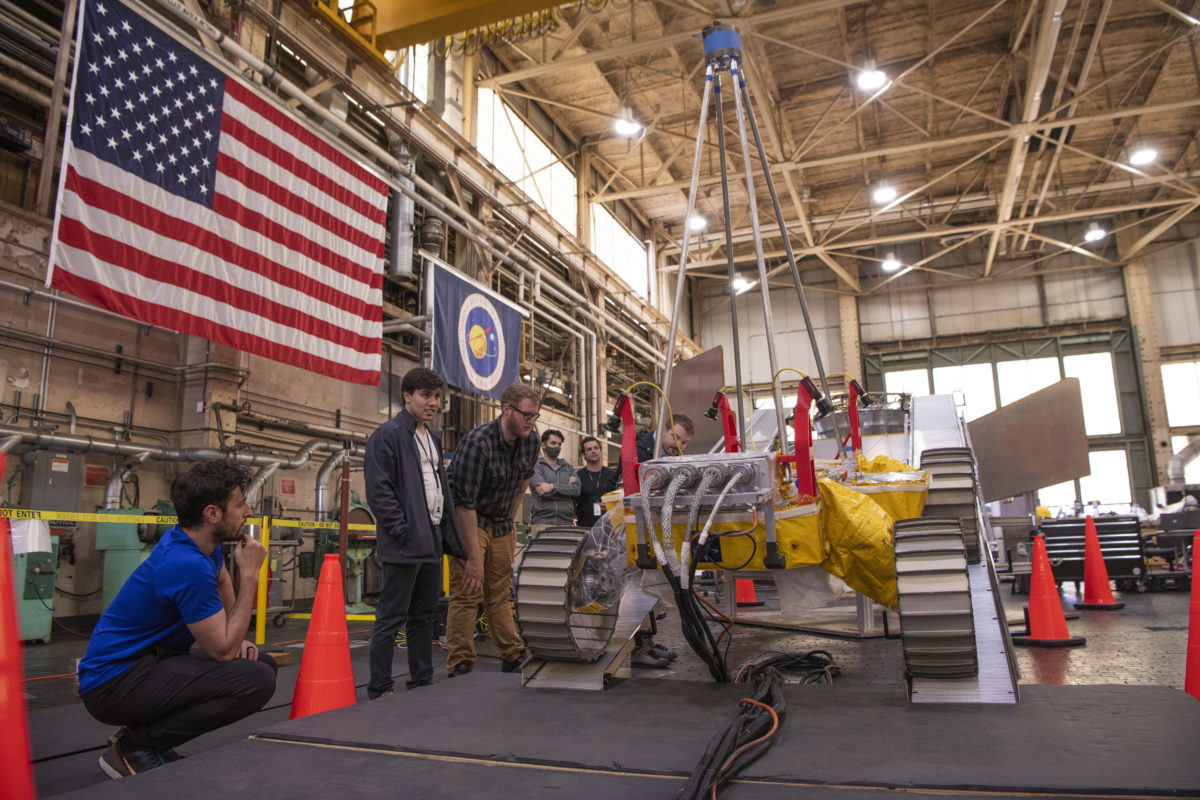
Last week, NASA held a public test of its Volatiles Investigating Polar Exploration Rover (VIPER) at the Glenn Research Center in Cleveland. The rover will have its delivery supported by North Shore-based Astrobotic’s Griffin lunar lander and will lead new efforts in searching for water on the moon beginning in 2024.
The test, which displayed and verified the rover’s ability to safely and effectively exit the lander after touchdown, was the latest mark of progress in a mission that started in 2020, when NASA announced it would give Astrobotic $199.5 million to develop the lander. It’s one of at least two Pittsburgh startups working with NASA, after Bloomfield Robotics announced a collaboration to bring its robotic farming cameras to the International Space Station last spring.
“It is an enormous honor and responsibility to be chosen by NASA to deliver this mission of national importance,” Astrobotic CEO John Thornton said in a statement at the time of the award announcement. “Astrobotic’s lunar logistics services were created to open a new era on the Moon. Delivering VIPER to look for water, and setting the stage for the first human crew since Apollo, embodies our mission as a company.”
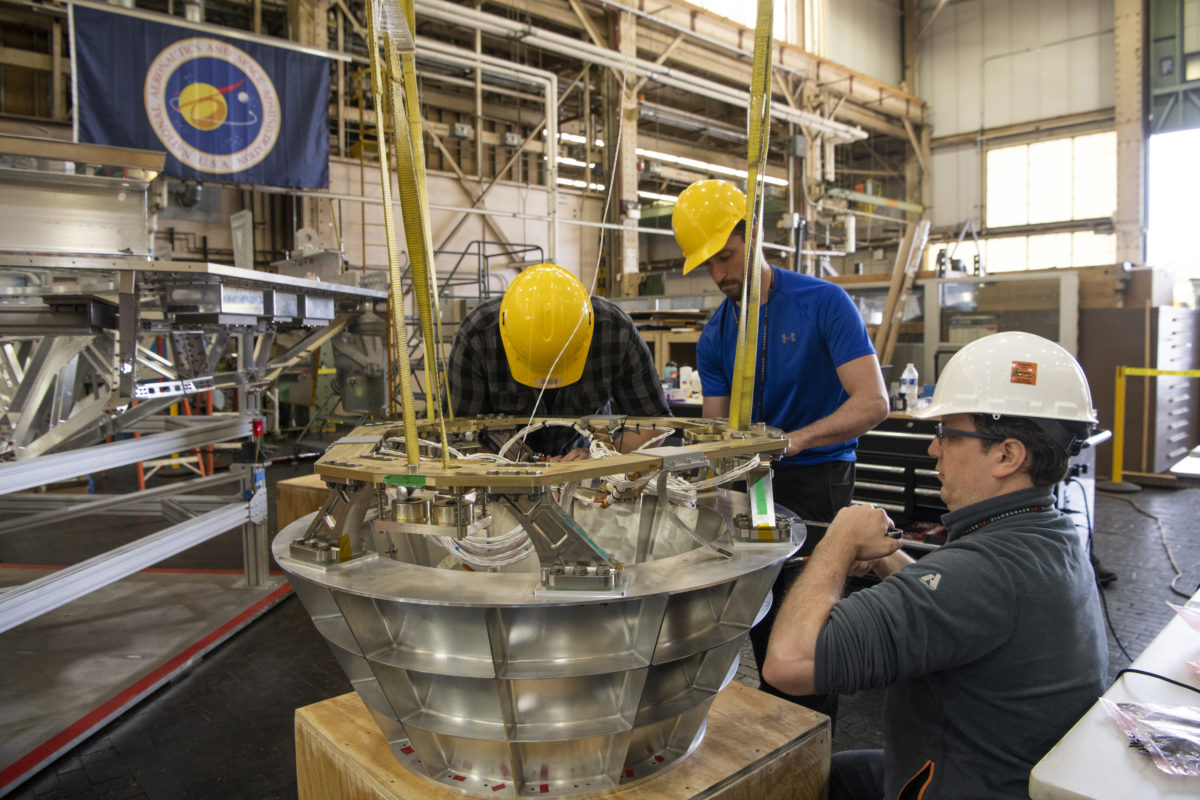
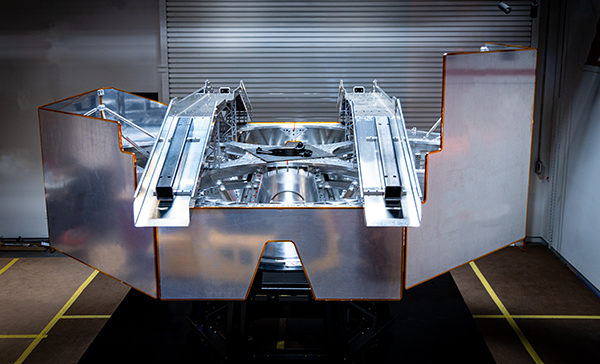
Astrobotic announced the official completion of the Griffin lunar test model earlier this year, with the final flight build slated to begin later this year. The test model alone weighs over 13,000 pounds, and is the largest lunar lander since the Apollo Lunar Module, which had its last launch at the end of 1972.
Last Thursday’s tests weren’t the first successful demonstration of the rover’s egress from Astrobotic’s lander. But a press release on the event noted that they were the most realistic tests yet, using prototypes that reflected the mobility systems of the rover and lander while stripping both for their heavier components. Subtracting those parts from the prototypes more closely simulated what the vehicles’ mobility will actually look like on the Moon, compensating for the lower amount of gravity there.
Overall, the test was successful in demonstrating the functionality of the rover and lander systems. But future tests are still required to more closely simulate the conditions on the moon. Those will take place at the Regolith Testbed at NASA’s Ames Research Center in Silicon Valley, which can reproduce the terrain and lighting of the environment on the Moon. To catch a glimpse at the tests in Cleveland last week, check out the video below.