The Predictive Healthcare team at Penn Medicine has developed and released an open-source tool to help hospitals plan for patient increases and intake during the COVID-19 spread in the Philly area.
The tool, called CHIME, or COVID-19 Hospital Impact Model for Epidemics, uses SIR modeling, which computes the theoretical number of people infected with a contagious illness in a closed population over time to predict outcomes.
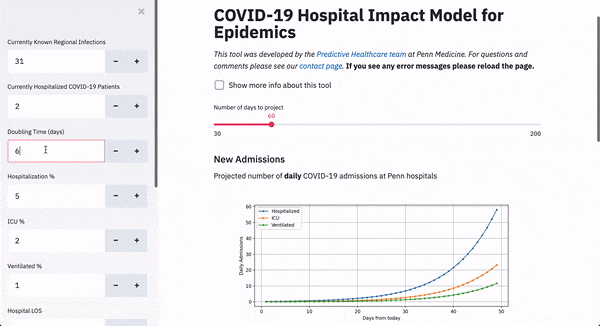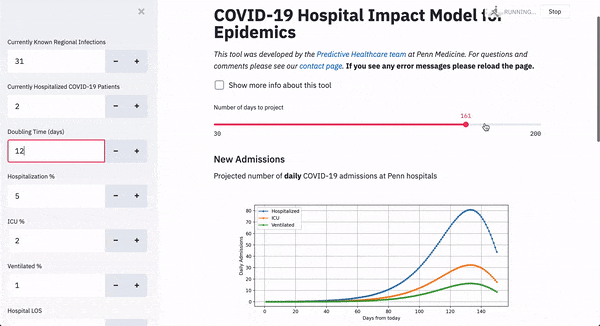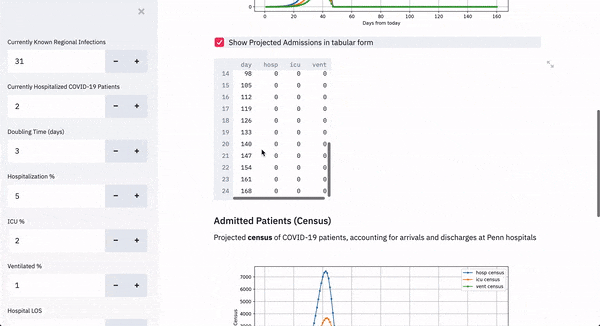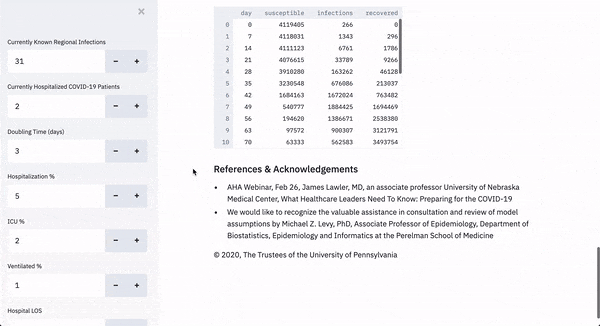
It’s currently set up to help Penn’s operational leaders with up-to-date projections of what additional resources will be required, and estimate of how many patients will need hospitalization, ICU beds and mechanical ventilation.
Essentially, it will help inform Penn’s readiness responses and mitigation strategies, said Michael Becker, a senior data scientist at Penn Medicine. Beckers said a colleague began developing the tool on Friday, and the team worked on it over the weekend to ready it and release it for public use.
Code for Philly has also helped out on the project, Becker said, and both camps are welcoming help.
The tool is currently set up to serve Penn Medicine, but because it’s open source, it could be modified for each healthcare center’s specific population. The methodology behind the tool isn’t new — similar approaches were used in previous outbreaks — but newer technology has allowed for quicker creation and sharing abilities, Becker said.
The tool is most useful in a shorter-term capacity.
“It’s allowing hospital systems to assess their needs now, and if things don’t change, how they can get more resources, ICU beds, things like that,” he said.
One of the most useful parts of the tool is predicting doubling time, showing how quickly the virus will spread between people. What will happen in a few weeks from now will depend on what the city’s population is doing now in terms of practicing social distancing, Becker said.
“The further out in time we look the more uncertainty there is,” he said.
If the city sees an explosion in the virus, hospitals and healthcare workers will have to make some very tough decisions about rationing care, an issue doctors in other places in the world have already confronted.
For those working outside of the Philadelphia area, the tool is still effective, but three main factors — currently known regional infections, currently hospitalized COVID-19 patients and hospital market share — must be known.
“We are currently trying to deal with demand, but we know it will be increasing a lot,” Becker said.
Before you go...
Please consider supporting Technical.ly to keep our independent journalism strong. Unlike most business-focused media outlets, we don’t have a paywall. Instead, we count on your personal and organizational support.
Join our growing Slack community
Join 5,000 tech professionals and entrepreneurs in our community Slack today!

The man charged in the UnitedHealthcare CEO shooting had a ton of tech connections

From rejection to innovation: How I built a tool to beat AI hiring algorithms at their own game

How a laid-off AI enthusiast pivoted to become a founder — while holding down a day job